Low back pain affects many people, regardless of age and profession. Chargers and office workers, young mothers and retired gardeners, writers and even athletes suffer from them. In any of them, pathological changes can occur in the bone and cartilaginous tissues of the vertebrae, leading to compression (compression) of the spinal nerve roots, causing severe pain.
But painful sensations are only external manifestations of the disease. It is often accompanied by other pathological syndromes that require mandatory treatment, the absence of which often leads to disability and the ability to self-care. In other words, a person is disabled.
Description of the disease
Osteochondrosis is caused by an unnatural compression of the spine, which causes compression of the intervertebral discs and the adjacent tissues of the ligamentous apparatus. When squeezed, a liquid comes out of the discs, which is responsible for their plasticity and is a source of tissue nutrition with the necessary microelements. With prolonged negative impact, the fibrous annulus of the intervertebral discs loses its elasticity and density, and then breaks, leading to compression of the nerve endings. This is the reason for the appearance of pain, which is often accompanied by edema.
In addition, the outer edges of the vertebrae, with an incorrectly distributed load, are filled with osteophytes - growths of bone tissue. They also cause pain and restrict movement in the spine, compounding the problem.
That is, the disease occurs most often with such loads on the spine, which are incorrectly distributed or stereotyped, monotonous and regularly repeated.
Causes of occurrence
Do not assume that only intense physical activity or a sedentary lifestyle, in which the muscle structure is weakened, leads to osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. This also happens with very active people who play sports or who work daily in their summer house. If your movements are monotonous (lifting the bar, digging the ground), pressure is produced at the same points, in the area of which the cartilage tissue is gradually destroyed.
There are other reasons too. Among them:
- violation of calcium metabolism in the body;
- excess weight or its severe fluctuations in any direction when following a strict diet, pregnancy, a sharp change in hormonal levels;
- injury or curvature of the spine (scoliosis);
- one-time severe hypothermia or regular exposure to cold, humidity;
- depressive conditions, stress;
- constant physical overhead;
- bad inheritance.
Pay attention. Any rigid diet based on the use of a product or a critical reduction in caloric intake leads not only to a strong weight loss, but also to the appearance of a deficiency of valuable trace elements in the body. Which is also bad for muscles and bones.
Symptoms
Osteochondrosis is rarely detected early, since in the initial stage it is asymptomatic. More precisely, there are symptoms, but they are difficult to associate with spinal problems. Therefore, most of the time they are discovered by accident during a comprehensive exam for other health problems.
There are four stages of development of the disease. Let's describe the symptoms for each.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| First | In the first stage, the sweating processes are interrupted, a person experiences general malaise and rapid fatigue. Some patients speak of a previously unusual shiver of the feet. |
| Second | In the second stage, intermittent back pain occurs, indicating that the destruction of cartilage tissue begins. |
| Third Party | The third stage is characterized by already visible changes. An intervertebral hernia may appear, often a curvature of the spine occurs, and in some cases a hump grows. |
| Fourth | The fourth stage is the most difficult, when there is no need to talk about a complete cure due to irreversible changes in the skeleton. In addition to the proliferation of osteophytes and the displacement of the vertebrae, causing acute pain, problems arise in other organs of the pelvis. Often the patient loses control over the urination and defecation processes. |
Disease treatment
Methods of treatment of osteochondrosis are selected depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of pain. Conservative treatment provides good results only in the initial stages. For example, if osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine was detected early on, you can get rid of it with the help of special physical exercises, correction of physical activity and body weight, swimming, taking vitamin-mineral complex preparations.
When pain occurs, this is no longer enough. It must be eliminated along with the cause of its appearance. Why are medicines, traditional physiotherapy techniques and even alternative medicine methods used? And in the later stages, only surgical treatment is possible.
Physiotherapy
To relieve pain and swelling, improve the effect of medications and reduce their dose, hardware physiotherapy methods are used such as:
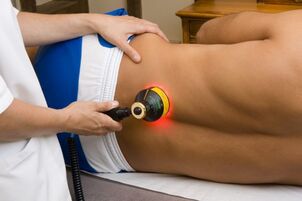
- ultrasound;
- laser;
- magnetic field effect;
- electrophoresis;
- manual therapy, massage.
Pay attention. Massage helps relieve muscle spasms, improves blood circulation in the area of affected intervertebral discs, and frees pinched vessels and nerves. This is done only with the help of the hands, but vacuum massage is contraindicated in this disease.
Shock wave therapy
UHT is a relatively new treatment method, the implementation of which uses the most advanced equipment with programmable shock wave dosing and a system for their guidance.
The point is that the shock waves destroy the osteophytes and restore the cartilage tissue. But the healthy bones of the spine, as well as the main arteries, can also be damaged. Therefore, it is very important to ensure that this technology is well developed in the hospital and that the treatment is carried out by a highly qualified and licensed specialist.
Alternative Therapy Methods
In addition to the standard methods for treating osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, there are also non-traditional methods. These methods are constantly being studied and are already being applied in many clinics. These mainly include:
- hirudotherapy or leech therapy that help relieve inflammation and improve blood circulation;
- Acupuncture or acupuncture is an effective way to relieve pain, muscle tension, and inflammation. It consists of the introduction of special needles in certain biologically active points of the body;
- ozone therapy: injection of a mixture of ozone and oxygen. With the correct dose, this method inhibits the growth of osteophytes and relieves painful muscle tone.
Parallel to these treatment methods or to record the results obtained with their help, a course of kinesitherapy and therapeutic gymnastics is carried out.
Surgical techniques
If the disease begins and conservative treatment does not alleviate the patient's condition, surgical methods are used. You can not do without them if after several months of active treatment it was not possible to relieve pain and improve the general condition of a person. And especially in those cases in which problems appeared such as decreased potency in men, alteration of the pelvic organs, numbness of the perineum.
- Endoscopic microdiscectomy: removal of a herniated disc. This is a minimally invasive surgery that relieves compression on the spinal cord or nerve root.
- Laser reconstruction of intervertebral discs can hardly be considered an operation. During the procedure, which is performed under local anesthesia, a fine needle is inserted into the affected disc, through which it is irradiated with a laser that stimulates the division of cartilage cells.
- Foraminotomy is an operation to remove the processes of a vertebra or part of a disc, the purpose of which is to free a pinched nerve.
- Vertebroplasty: the injection of bone cement into the destroyed spinal tissue to strengthen it.
- Osteotomy: removal of diseased vertebrae and discs with subsequent replacement by prosthesis.
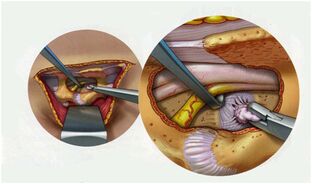
There are other methods aimed at stabilizing vertebrae, decompressing them, removing osteophytes, etc. Any of them requires a long recovery period. After the surgical treatment of the spine, the patient should not stand up, walk, bend over or experience physical stress for a long time. This leads to muscle relaxation and partial loss of motor functions, which require support and rehabilitation. Therefore, at the end of the postoperative period, a period of recovery and rehabilitation begins, the task of which is to fully restore motor functions and prevent complications in the pelvic organs.
At this stage, some of the conservative treatment methods described above are applied, correct posture is developed, habitual movements are corrected. In this case, the patient is recommended to wear a special fixation brace. After that, an individual set of exercises is worked out, which must be performed daily and for life to avoid relapse of the disease.

























