
Osteochondrosis is one of the most frequently diagnosed pathologies of the spine. This pathology has a degenerative-dystrophic origin, affects the intervertebral discs, which leads to their structural and external modifications. Doctors define three types of disease: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar osteochondrosis, based on the location of the disorders in the spine. If we talk about the statistics of the identified pathologies, it is believed that thoracic osteochondrosis is less common than other types. This is due to the peculiarities of the structure of the human spine in the thoracic region: the intervertebral discs of this part of the back have limited mobility, which significantly reduces the probability of their traumatic injury.
What is thoracic osteochondrosis?
Identifying the disease is difficult, since its symptoms are usually similar to pathological changes in other organs: heart, stomach, etc. Thoracic osteochondrosis is dangerous in its consequences, therefore its early detection provides more chances for timely correction and prevention of undesirable consequences. The disease is diagnosed with the same frequency in patients of both sexes of different ages, including children. Let us dwell in more detail on the causes of thoracic osteochondrosis, its symptoms, drug and home treatment methods.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine manifests itself as degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the structure of the bone, cartilaginous tissue of the vertebrae, which provokes the development of destructive processes in them. In addition to the vertebrae themselves, the intervertebral discs suffer: they stratify, decrease in size, as a result of which the nerve endings in the intercostal space are pinched. All of this together affects the normal function of the spine. Treatment started at the wrong time aggravates the situation, which is later resolved exclusively with the help of a surgical operation, which cannot always be resolved by the patient for various reasons.
Osteochondrosis of the chest can provoke the development of quite serious and dangerous diseases and conditions. It often becomes the cause of pneumosclerosis, narrowed blood vessels, dysfunctions of the genitourinary system, cancerous pathologies, etc. If osteochondrosis progresses rapidly, this usually limits a person's physical capabilities - it is difficult for him to walk, work, and do his job freely. habitual activities.
With the development of osteochondrosis in patients, the bone component of the vertebrae is initially affected, then the cartilaginous, and finally the connective tissue and adjacent muscles.
If signs of osteochondrosis appear in childhood or adolescence, adolescence, then this is a dangerous situation, because it indicates that the person's musculoskeletal system began to age without being fully formed and developed. Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in a child is rarely diagnosed. But the detected disease often indicates that there is some other dangerous disease.
The pathology is found approximately with the same frequency in both men and women. There are also no age-specific priorities. But it is worth noting that women are more prone to the disease during the period of hormonal changes in the body - menopause.
If you start treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in the early stages, the therapy is much more likely to give a positive result.
The degree of the disease and the characteristic symptoms.
The development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is gradual, several stages are different. For the correct organization of the treatment process, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms of its development and progression.
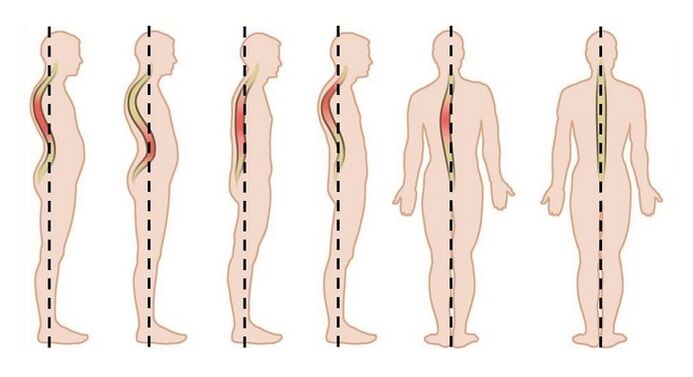
- The initial stage of degenerative-dystrophic processes that occur in the spine is characterized by a slight decrease in the size of the intervertebral discs. Minor cracks begin to appear on the surfaces of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral discs. The disc may be slightly out of the spine. At the same time, first-degree thoracic osteochondrosis does not reveal itself as painful sensations, often a person is unaware of an incipient dangerous disease. With the help of computed tomography, the bulging of the discs (their slight loss) is detected.
- If a person has grade 2 thoracic osteochondrosis, painful manifestations on the back begin to appear in the chest area. This is explained by the fact that the nerve fibers are pinched. The musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the back, that is. Muscular corset, provides optimal support of the spine in the correct anatomical shape. To prevent spinal instability, it is extremely important to symmetrically shape the muscular structures of the back. Otherwise, there is not only a violation of posture, curvature of the spine, but also excessive mobility of its individual elements. It is due to the increased mobility of the vertebrae that the nerve fibers exiting the spine through the intervertebral space are pinched. How does osteochondrosis manifest itself in the second stage? Back pain in the second stage of thoracic osteochondrosis necessarily appears. It has different characteristics: it can be pulling for a long period of time or short term, in the form of seizures. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the nerve endings are directly compressed in the muscles, which are regularly in increased tone.
- The morphological signs of third degree thoracic osteochondrosis are very pronounced, affecting all structural anatomical components of the spine. The patient has the following pathological picture: there are hernias and protrusions of the intervertebral discs, the muscles and ligaments become inflamed, tears appear, the vertebrae are displaced, signs of osteoarthritis of the vertebral joints develop. The clinical picture of spinal disease in the third stage is very diverse. In addition to the fact that a person really has pain in osteochondrosis of the chest, the patient loses the tactile reaction of the part of the body through which the damaged nerve passes; he has disorders of the autonomic nervous system, which are accompanied by dysfunctions of the respiratory and circulatory systems. It becomes difficult for him to breathe, there is pain in the heart, arrhythmia, shortness of breath. In addition, the patient develops arthrosis of several joints at once, and pathological disorders begin in the functioning of the organs that are located in the chest area. Similar symptoms appear when the intervertebral fissure decreases by two-thirds of its height. Its size is evaluated using a chest radiograph, which is performed in two views: straight and lateral.
- With the development of degenerative processes in the spine up to fourth-degree osteochondrosis, the intervertebral cleft narrows to a minimum distance, such dangerous conditions as spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis (characterized by pathological changes in the intervertebral joints), spondylolisthesis (the vertebrae are crooked or displaced) develop. The body mobilizes its compensatory capacities to reduce the static and dynamic load on the spine, to avoid injury to the anatomical elements, so the vertebrae grow, flatten and grow together. The damaged area of the fibrous ring is replaced by a bony structure, osteophytes (bone outgrowths) are formed, due to prolapse of the vertebral disc, the spinal cord narrows, the nerve endings are strongly compressed, the motor activity of the thoracic spine is significantly limited, the person constantly hurts in the chest region from the back.
- As a result of the progression of the disease, the patient has low back pain in the lower back (lumbago), the legs are totally or partially paralyzed, the person loses the ability to work, becomes disabled.
Various symptomatic manifestations of the disease depend on various reasons, including a person's genetic predisposition. The same symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine fail in different patients in different ways. There is an objective explanation for this: various causes, conditions of occurrence and the general state of human health lead to osteochondrosis. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in men appear somewhat earlier than in women. The main reason for this phenomenon lies in the physiological structure of the female body: the hormone estrogen protects the intervertebral discs, therefore, especially favorable conditions for the disease arise during changes in the hormonal background (during pregnancy, menopause).
Many are interested in whether they are brought into the army with osteochondrosis. If the recruit has osteochondrosis of the first degree, he will be drafted into the army. In the event that a young man has a pronounced symptomatology of the disease, it is observed by a neuropathologist, then it is likely that there is a delay, in a neglected state (if there is polysegmental osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine), they may not call absolutely. .
Reasons for the appearance
Thoracic osteochondrosis at the beginning of its appearance practically does not manifest itself at all. However, you need to know why it may appear. The following reasons provoke pathology:
- Regular static or dynamic overexertion of the spine due to active strength training in professional athletes or people involved in sports without the necessary load control.
- Traumatic damage to the bone, the articular elements of the spine often leads to the fact that they do not fuse properly and quickly collapse. Any injury to the spine is aggravated by pathological changes in the functioning of the structures of the nervous and circulatory systems. The necessary supply of nutrients to the bones is often restored over a very long period of time.
- Poor posture, congenital or acquired curvature of the spine, leading to an unbalanced effect on the intervertebral discs.
- Rough lifting of weights, when the overwhelming part of the load falls on the chest region of the back. If a person constantly performs such movements, then the probability of developing thoracic osteochondrosis is high.
- Endocrine system disorders. In the event that the metabolic processes in the body are disturbed, all other organs and tissues do not receive the necessary nutrients and their regeneration is also incorrect.
- Genetic prerequisites for possible pathological processes in the vertebrae, intervertebral discs. In this case, thoracic osteochondrosis manifests itself in absolutely any age category.
- Insufficient physical and physical activity of a person, sedentary work. The muscular structure of the back in this situation is weakened, the nutrition of the tissues deteriorates, the flexibility of the spine decreases, and the risk of developing thoracic osteochondrosis increases significantly.
- Underdevelopment of all tissues of the musculoskeletal system, causing degenerative disorders in the spine. The cause is an excessive and unbalanced load on the spine.
- Various pathological changes in the intervertebral discs. They can become thin or, on the contrary, grow, osteophytes can appear in them, interfering with the functioning of the joints, in addition to damaging the blood vessels and exerting compression on the nerve fibers. The development of intervertebral hernias often provokes the progression of osteochondrosis.
- Inflammatory processes in the spine or nearby muscles often cause signs of thoracic osteochondrosis in women and men.
- Poor blood supply to the spinal cord, due to the fact that the veins and arteries narrow or squeeze.
- The consequences of infectious diseases are the development or exacerbation of osteochondrosis.
- Hypothermia, abuse of bad habits, nutritional imbalance.
- Separately, psychosomatics is distinguished, that is, constant stress, nervous excitement can also cause osteochondrosis.
There are quite a few reasons for the development of thoracic osteochondrosis, therefore, in order to prevent its development, you need to pay attention to prevention.
Common symptoms
Symptoms of breast osteochondrosis in women and men are similar. Usually a progressive disease during an exacerbation is manifested by the following symptoms.
- Strong pain in the thoracic spine. They arise from a long stay in an uncomfortable position during physical work.
- Root syndrome, as a result of compression of the nerve endings.
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- The appearance of spasms in the muscles of the back.
- An altered state of the heart muscle, in which pain is not relieved by taking special medications.
Also, during an attack of thoracic osteochondrosis, the patient may experience atypical symptoms: tachycardia, dizziness, heartburn, increased or decreased blood pressure. Body temperature, as a rule, does not change.
Diagnostic techniques
If the doctor assumes that the patient has osteochondrosis, he will propose to undergo the following studies to diagnose the pathology.
- X-ray examination, during which they determine: the limits and size of the intervertebral discs, existing bone growths, changes in the shape of the vertebrae, etc.
- Radiography with a contrast agent allows you to assess the degree of destruction of the discs in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging shows a layer-by-layer visualization of altered structures. These techniques are used in the most difficult situations.
- With the help of electromyography, the neurological signs associated with a disease in the thoracic region are differentiated.
The main rules of treatment
When treating osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, the following key points are noted:
- With the initial manifestations of signs of osteochondrosis, you can prevent its further development by correcting your posture.
- Any symptoms of the disease, even minor ones, require conservative therapy.
- To achieve a positive result in treatment, a systemic and long-term application of techniques in addition to drug therapy is required.
- If the disease is neglected, surgery is required.
When deciding how to treat osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, the doctor will take into account the stage of development of the disease, the individual characteristics of the patient and possible side reactions of the body.
Drug treatment
Conservative therapy involves the use of the following groups of drugs.
- To reduce the manifestation of pain and inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics or glucocorticosteroids are prescribed. They are available in different drug forms (tablets, solutions for injections, ointments), therefore, what exactly to treat the disease the doctor will advise.
- Chondroprotectors are used to stimulate the restoration of cartilage tissue.
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are used to relieve muscle spasms.
- To relieve excruciating back pain, the patient can be offered to administer injections for osteochondrosis, to carry out a blockage with the help of anesthetic drugs.
As a combined treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis, the possibilities of the following additional treatment methods are widely used.
- With the help of acupuncture, you can quickly get the result - pain relief. The advantages of the technique include: high efficiency in a short time, a rare occurrence of side reactions of the body, an insignificant list of contraindications, a painless technique. Acupuncture is not practiced if a person is diagnosed with the presence of malignant neoplasms, there are mental disorders, during an exacerbation of inflammation and pregnancy. The duration of treatment is selected individually.
- Through the possibilities of manual therapy, blood supply to damaged areas of the body improves, pain intensity decreases, muscle spasm is eliminated, ligaments are restored, the development of osteochondrosis slows down.
- Treatment of osteochondrosis with the help of physiotherapy is practiced everywhere, since, using them, drugs are injected into the sore spot. This is how it is used, for example, electrophoresis with NSAIDs, glucocorticosteroids, etc. In addition to electrophoresis, UHF, magnetotherapy, and vacuum are often prescribed. The main objective, which is achieved through physiotherapy techniques, is to improve blood circulation in the painful area.
- To relieve spasms in the muscles of the back, a course of massage is often prescribed. Classic massage is used during remission and vibration massage - in an acute period. If the patient has an intervertebral hernia, it is not recommended to use massage techniques.
- Physiotherapy is of great importance in treatment. The specific set of exercises in each case is selected by the doctor individually.
- During the treatment of osteochondrosis, diet is important. In the patient's diet, it is imperative to include protein in the required amount, chondroitin (for this you need to eat jelly, jelly meat, aspic dishes), vegetables, fruits. You cannot overeat; exclude the use of fried and fatty foods.
How to treat chest osteochondrosis at home
Treatment with home remedies can also be practiced, but before using any of them, you should consult your doctor. The following recipes are popular.
- To prepare an infusion of celery root, take 3-4 g of raw materials, grind, pour 1 liter of boiling water. After 8 hours, filter the infusion, drink up to three times a day with a dessert spoon.
- To prepare the broth, take 2-3 sunflower roots, cut them into pieces of about 1 cm, pour three liters of boiling water and boil for another 3 minutes. The remedy is used as a tea.
- At home, you can prepare an ointment to rub the sore spots. 150 g of pork fat are mixed with 2 tbsp. l. wax, heated for 20 minutes in a water bath, then add 1 tbsp. l. fir oil, continue to heat the same amount, then add 1 tbsp. l. ammonia. The product is stored in a glass container in a cool place.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis at home is usually used in the mild period or as an adjunct to medications during an exacerbation.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a disease that must be taken seriously to avoid negative consequences. For your successful treatment, you should carefully consider the advice of a doctor and follow it with discipline.

























